Why does the sea look Teal? 90% of people don't know
2023-05-24
We know that water is colorless, but underwater images often have a background of blue or green. Why is this? This is actually caused by the absorption, reflection, and scattering of sunlight by seawater. Sunlight is a combination of seven colors of light, composed of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and purple. Water reflects blue light, so the seawater seen is blue.
We know that water is colorless, but underwater images often have a background of blue or green. Why is this?
This is actually caused by the absorption, reflection, and scattering of sunlight by seawater. Sunlight is a combination of seven colors of light, composed of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and purple. Water reflects blue light, so the seawater seen is blue.

When the sunlight shines on seawater, the longer wavelengths of red, orange, and yellow light are absorbed by the seawater, while deeper waters absorb green light. The remaining blue and purple light with shorter wavelengths will scatter in all directions or reflect back when they encounter water molecules. At the same time, because the human eye is not sensitive to the purple light reflected by seawater, it does not feel that seawater is purple. What the human eye sees is the light scattered or reflected from this part. The deeper the seawater, the more blue light is scattered and reflected, so the ocean appears blue.

We see scenery on land, and during this process, the medium through which light passes is air. But when shooting underwater, the medium for light transmission becomes water. When the scene passes through the underwater medium to the human eye or other sensors, the object basically loses the attribute of "color", and most of the image backgrounds are Teal, as if covered with thick Teal "filters".
1
What is scattering
Scattering is a phenomenon where the surface curvature of an object illuminated by projected waves is large or even uneven, and the secondary radiation waves diffuse and distribute according to a certain pattern in the angular domain. It refers to the separation of molecules or atoms when they approach each other due to their strong mutual repulsion, forcing them to deviate from their original direction of motion before contact, which is commonly referred to as "scattering". Scattering refers to the phenomenon of light scattering towards the surrounding area caused by the non-uniformity of the propagation medium. For example, when a beam of light passes through diluted milk, it is white, but from the side and top, it is Baby blue.

The phenomenon where some light changes direction in multiple directions when passing through a medium such as dusty air or colloidal solution. It is called light scattering. When ultrashort waves are emitted into the ionosphere, scattering also occurs. When solar radiation passes through the atmosphere and encounters particles such as air molecules, dust particles, and cloud droplets, scattering occurs. But scattering does not transform Radiant energy into heat energy as absorption does, but only changes the direction of radiation, so that solar radiation spreads in all directions with the particle as the center. After scattering, a portion of the solar radiation cannot reach the ground. If solar radiation encounters air molecules with a diameter smaller than the wavelength, the shorter the wavelength of the radiation, the more severe it is scattered. The comparison between its scattering ability and wavelength is that for molecules of a certain size, the scattering ability is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength, and this type of scattering is selective. For example, the scattering ability is 1 at a wavelength of 0.7 micrometers, and 30 at a wavelength of 0.3 micrometers.
Therefore, when solar radiation passes through the atmosphere, light with shorter wavelengths is more scattered due to the scattering of air molecules. After rain, the sky becomes clear and the blue blue color is due to the short wavelength of blue radiation, which is easily scattered by the atmosphere. If solar radiation encounters particles larger in diameter than waves, although they are also scattered, this scattering is not selective, meaning that all wavelengths of radiation are equally scattered. If there is a large amount of dust or fog particles in the air, a certain range of long and short waves are equally scattered, resulting in a gray white sky.
II
What is the reflection of light
The reflection of light is a Optical phenomena. The phenomenon of light changing its direction of propagation at the interface and returning to the original material when it propagates to different substances. Light will reflect when it encounters the surface of water, glass, and many other objects. The phenomenon of light changing its propagation direction at the interface of two substances and returning to the original substance is called reflection of light.

The difference between reflection and refraction of light
The reflection of light: The phenomenon of light changing its direction of propagation at the interface of two substances and returning to the original substance, called light reflection. Understanding the reflection law of light can be summarized as follows: 1. In the reflection phenomenon, the reflected light, the incident light, and the normal are all in the same plane. 2. The reflected light, the incident light, and the normal are separated on both sides of the normal. 3. The reflection angle is equal to the incident angle, which can be summarized as: "Three lines are coplanar, two lines are separated, and the two angles are equal." When the reflected light of light enters another medium from one medium or propagates in the same non-uniform medium, The phenomenon of directional deviation is called refraction of light.
III
Is there a way to solve the distortion problem of underwater images?
From an optical perspective, the visible spectral range that the human eye can receive is about 380-780nm. Red light has a longer wavelength, around 700nm, and the wavelength is slightly longer than red light, which is called infrared; Similarly, the wavelength of purple light is about 400nm, which is slightly shorter than the wavelength of purple light. We call it ultraviolet light.

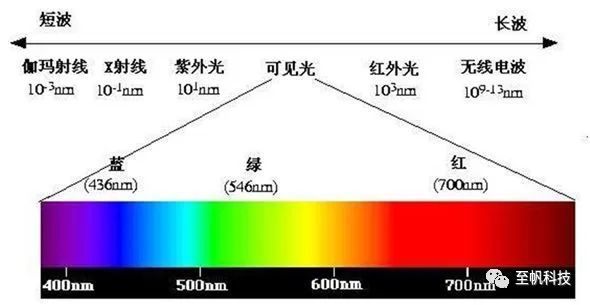
The attenuation characteristics of light in water are completely different from those in air. In underwater environments, different wavelengths of light have different attenuation rates when propagating underwater. Among them, in the visible light range, the penetration ability of red light with longer wavelengths is the weakest, and it disappears first at 3-4 meters underwater; Blue light has a shorter wavelength and a longer transmission distance in water; The light in most wave bands will be strongly absorbed and attenuated when propagating underwater. Only the blue-green light with a wavelength of 480 ± 30nm has the smallest absorption Attenuation coefficient and the strongest penetration ability in water, so this band is often called "underwater window".
The Exponential decay of light propagation in water leads to low contrast and fuzzy surface of the captured image, which is often the "behind the scenes" of the color distortion of underwater imaging. In such an environment, work efficiency is extremely low.
With the need of ocean development and the continuous progress of computer information processing technology, it has become possible to obtain clear and perfect underwater scene images by regulating the imaging process and subsequent processing of degraded images.
Image restoration algorithms mainly refer to modeling the degradation process of underwater images, estimating model parameters, and inverting the degradation process to obtain clear underwater images. The classic computer model for underwater imaging systems was proposed by McGladery in 1979.
The image received by the underwater imaging system consists of three parts: direct attenuation component, forward scattering component, and backward scattering component. Among them, the direct attenuation component refers to the light reflected directly from an object in water without being scattered by the medium; Forward scattering component refers to the portion of light reflected by an object that is still collected by the sensor at a small angle after being scattered and attenuated; The backscattered component refers to the part of the background light in the environment and the attenuated light scattered by surrounding objects that enters the sensor, in addition to the light reflected by the scenery. By relying on the prior information of the image and model parameters, real underwater scenes can be restored.
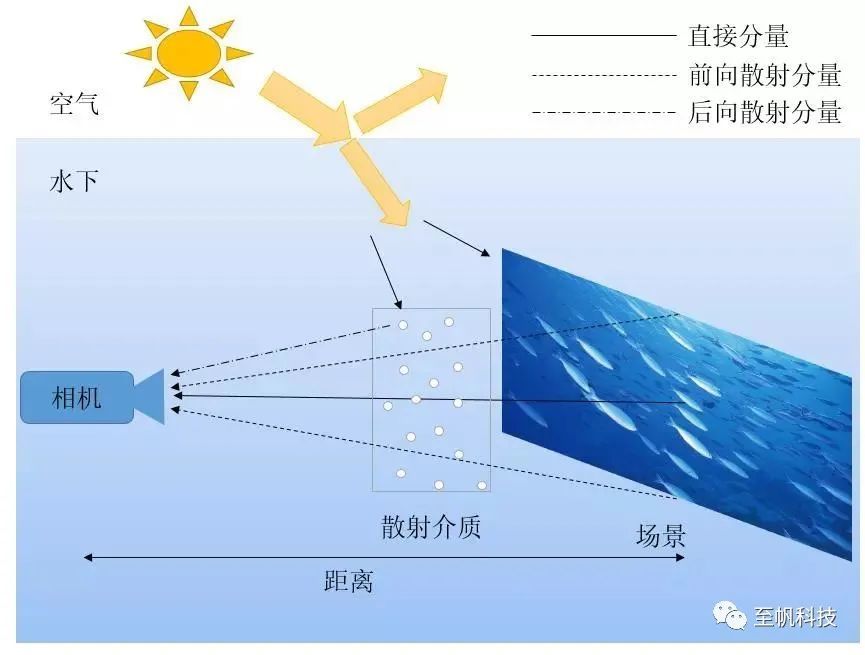
The restoration of underwater images mainly includes two parts: compensation and enhancement. Firstly, based on the attenuation characteristics of different wavelengths of light, compensate for channels with severe degradation and correct image chromaticity; Secondly, on the basis of chromaticity adjustment, the image is enhanced to enhance its contrast, resulting in a more eye-catching visual effect and more obvious image details.

Nowadays, more and more underwater robots have been put into use, and the ability to process image information is crucial for underwater robots to dynamically perceive the environment, quickly locate and track visual targets. Underwater robots equipped with image restoration technology can be directly applied to underwater observation and have broad application prospects in ocean engineering.
Previous page: not have
Next page: The editor takes you to understand the wide range of underwater camera applications
relevant content
2023-06-13

